Rain Detector Alarm Investigatory Project PDF Class 12
PDF Download Link Given Below
To Get the Link Scroll Down to end of this Page
INTRODUCTION
Since ancient times, mankind has skillfully utilized natural elements for various purposes. Water has been used for irrigation and hydroelectric power generation, wind for operating windmills and turbines, and the sun for drying, heating, and cooking when concentrated. Among these, sun drying is one of the oldest and most widely practiced methods.
Sun drying is carried out in farms, homes, industries, laboratories, hospitals, and other institutions for numerous reasons. It is used to remove moisture from materials, dry clothes and agricultural produce, assist in construction and sculpture work, and bring about certain chemical or physical changes. In the electronics and pharmaceutical industries, components and plant materials are exposed to sunlight so that ultraviolet rays can induce specific changes. At home, sunlight entering through windows helps eliminate dampness, improves ventilation, and maintains a healthy living environment.
However, unexpected rainfall can severely disrupt sun-drying activities. If materials are not retrieved promptly, they may become wet or damaged. Clothes drying on outdoor lines are particularly vulnerable to sudden rain showers.
To overcome this challenge, the design and construction of a rain detector Alarm becomes essential. This device provides an instant alert as soon as rainfall begins, giving users sufficient time to retrieve materials, close windows, and protect belongings. Rain water detectors also find applications in irrigation systems, home automation, communication networks, and automobiles, making them a practical technological solution in daily life.
AIM
To prepare a working model of rain detector alarm and to study its principle and working.
APPARATUS
- Cardboard
- 9V Battery
- Battery Clip
- Buzzer
- Rain Sensor Module
- Switch
- Connecting Wire
THEORY
A rain detector alarm is an electronic system designed to sense the presence of rainfall and convert it into an audible or visual warning signal. The device operates by detecting changes in electrical properties caused by the contact of rainwater with a sensing element. This system is based on basic concepts of electricity, conductivity, and electronic switching.
Rainwater is not pure; it contains dissolved salts, minerals, and impurities from the atmosphere. Due to this, rainwater exhibits electrical conductivity. The rain sensor consists of a set of closely spaced conductive strips mounted on an insulating base. Under dry conditions, there is no electrical connection between these strips, and the circuit remains inactive.
When rain falls on the sensor surface, water droplets accumulate between the conductive strips, forming a conductive path. This causes a change in the electrical resistance of the sensor, allowing current to flow through the circuit. The electronic circuitry connected to the sensor detects this change and responds by activating an output device such as a buzzer or alarm.
The alarm continues to operate as long as the sensor surface remains wet. Once the rainfall stops and the water evaporates or drains away, the conductive path is broken. As a result, the circuit returns to its original state, and the alarm automatically switches off. This automatic operation makes the rain detector reliable and efficient for real-time rainfall detection.
Thus, the rain detector alarm functions as a simple yet effective system that translates the physical presence of rain into an electrical signal, providing immediate alert and enabling timely protective action.
APPLICATION
- Weather Monitoring Systems:
Used to detect the onset of rainfall and provide early alerts in weather stations and environmental monitoring setups. - Automatic Clothes Drying Systems:
Helps in automatically covering or moving clothes indoors when rain is detected, preventing them from getting wet. - Smart Irrigation Systems:
Assists in controlling irrigation by stopping water supply during rainfall, thereby conserving water. - Automatic Window and Roof Control:
Used in homes, greenhouses, and vehicles to automatically close windows, sunroofs, or skylights during rain. - Agricultural Applications:
Protects crops, harvested grains, and farm equipment by triggering alarms or automated covers during rain. - Traffic and Road Safety Systems:
Helps in activating warning signals on roads or highways during rainfall to improve safety. - Industrial and Domestic Alarms:
Used as a simple rain alert system in industries, warehouses, and homes to protect sensitive equipment and materials.
Electronic and Robotics Projects:
Commonly used in educational projects and automation systems to demonstrate sensor-based control
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM
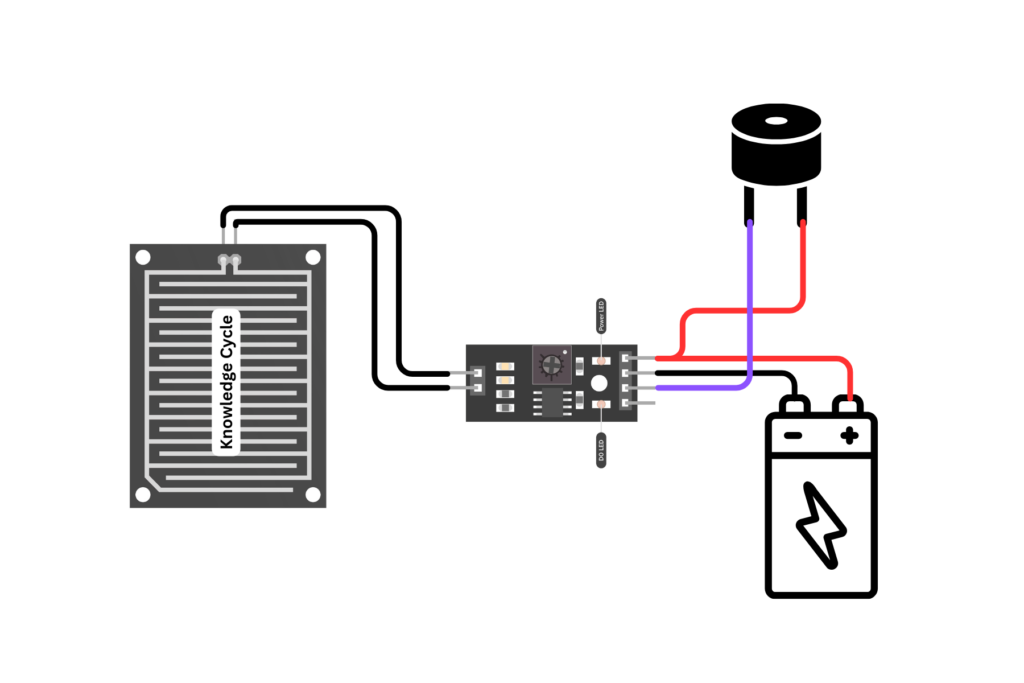
CONSTRUCTION
- Take a piece of cardboard sheet as the base of the model.
- Fix the rain sensor plate, comparator module, buzzer, battery, and switch on the cardboard according to the circuit layout.
- Connect the VCC pin of the rain detector module to the positive terminal of the 9V battery.
- Connect the GND pin of the rain detector module to the negative terminal of the battery.
- Connect the positive terminal of the buzzer to the VCC pin of rain detector module.
- Connect the DO pin of the rain detector module to the negative terminal of the buzzer.
- Attach a switch in series between the battery and the circuit to control the power supply.
- Ensure all connections are tight and properly insulated using tape or glue.
- Turn ON the switch and sprinkle a few drops of water on the rain sensor plate to test the working of the alarm. The buzzer should sound, indicating detection of rain.
WORKING PRINCIPLE
The rain detector alarm module works on the principle of change in electrical resistance due to the conductive nature of rainwater. The module mainly consists of a rain sensor plate and a control circuit. The sensor plate contains parallel metallic conductive tracks, usually made of copper, separated by small gaps. Under dry conditions, these tracks remain electrically isolated, resulting in very high resistance and no current flow through the circuit, keeping the alarm inactive.
When rain falls on the sensor plate, water droplets accumulate on its surface and bridge the gaps between the conductive tracks. Rainwater contains dissolved salts, minerals, and impurities, which make it a weak conductor of electricity. Due to this, the resistance between the tracks decreases and a small current start flowing through the sensor. This current generates a voltage signal at the sensor output, the level of which depends on the amount of rainfall.
The output voltage is fed to a comparator circuit, commonly using a comparator IC such as LM393. The comparator compares the sensor voltage with a pre-set reference voltage adjusted using a potentiometer. When the sensor voltage exceeds the reference value, the comparator changes its output state and activates an alarm device such as a buzzer or LED. Thus, the rain detector alarm module converts the presence of rain into an electrical signal and provides an immediate alert, making it useful for applications like weather monitoring and automatic control systems.
OBSERVATION
- When the switch is OFF, no current flows in the circuit and the buzzer remains silent.
- Under dry conditions, the rain sensor plate shows high resistance and the alarm does not activate.
- When water droplets are sprinkled on the rain sensor plate, the resistance between the conductive tracks decreases.
- As soon as water connects the tracks, the buzzer turns ON, indicating the detection of rain.
- The intensity of the buzzer sound increases with an increase in the amount of water on the sensor plate.
- When the sensor plate dries again, the resistance increases and the buzzer turns OFF automatically.
CONCLUSION
The rain detector alarm project has been successfully designed and demonstrated to detect rainfall using the conductive nature of rainwater. The working model clearly shows how a simple sensor and electronic circuit can convert the presence of rain into an audible warning signal. This allows timely action to be taken, such as collecting drying materials, closing windows, or protecting sensitive equipment from rain damage.
Through this project, a clear understanding of basic concepts like electrical conductivity, sensors, and alarm circuits is developed. The model is economical, easy to construct, and reliable in operation, making it suitable for educational purposes as well as practical applications. Overall, the rain detector alarm highlights the usefulness of simple electronic systems in solving everyday problems efficiently.
PRECAUTIONS
- The rain sensor should be placed in an open area where rain can fall directly on it.
- Ensure all electrical connections are tight and properly insulated to avoid short circuits.
- Use the correct voltage power supply to prevent damage to electronic components.
- Keep the circuit away from excessive water contact, except for the sensor plate.
- Dry the sensor properly after use to maintain accurate and reliable performance.
- Handle electronic components carefully to avoid physical damage

